Understanding the Android Ecosystem
Setting Up Your Android Development Environment
Required Tools and Software
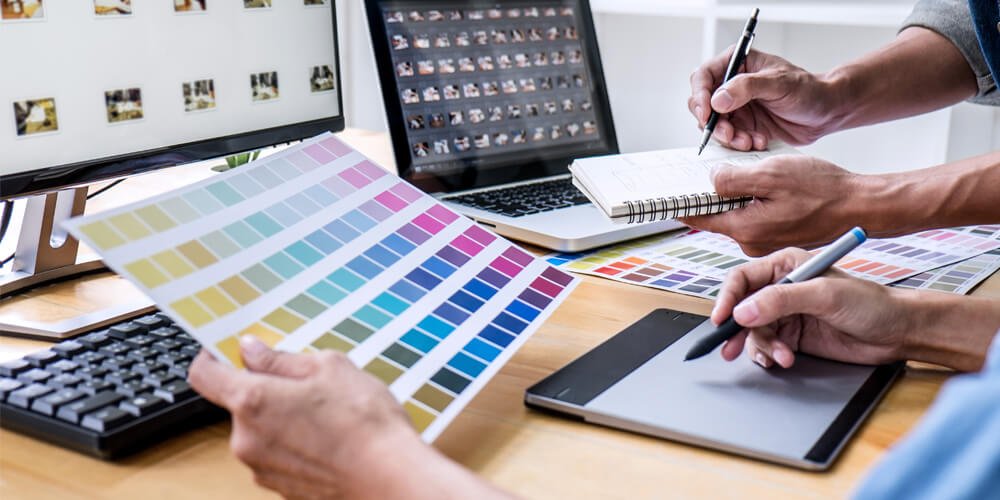
Before diving into code, it’s essential to set up a reliable and efficient development environment. This will serve as your workspace for designing, developing, testing, and debugging your applications.
Android Studio: The official IDE for Android development. It comes with everything you need including code editors, emulators, and debugging tools.
Java Development Kit (JDK): Required for compiling Java-based Android apps.
Android SDK: Provides the API libraries and developer tools necessary to build, test, and debug Android apps.
Emulator or Physical Device: For testing your apps during development.
Gradle: A build automation tool that helps manage project dependencies and build configurations.
Visual Studio Code
Lightweight code editor with Android plugin support build configurations of Visual studio.
Java was the original official language for Android and is still widely used. It offers strong community support, excellent documentation, and robust performance.

Firebase Console
Backend services like authentication, real-time database, crash reporting, and analytics.
Kotlin is now the preferred language for Android development, officially supported by Google. It is concise, expressive, null-safe, and interoperable with Java.


Git and GitHub
Version control tools for managing code changes and collaboration with github.
Used for performance-critical applications, especially in game development. Android supports native code using the Native Development Kit (NDK) with android languages.
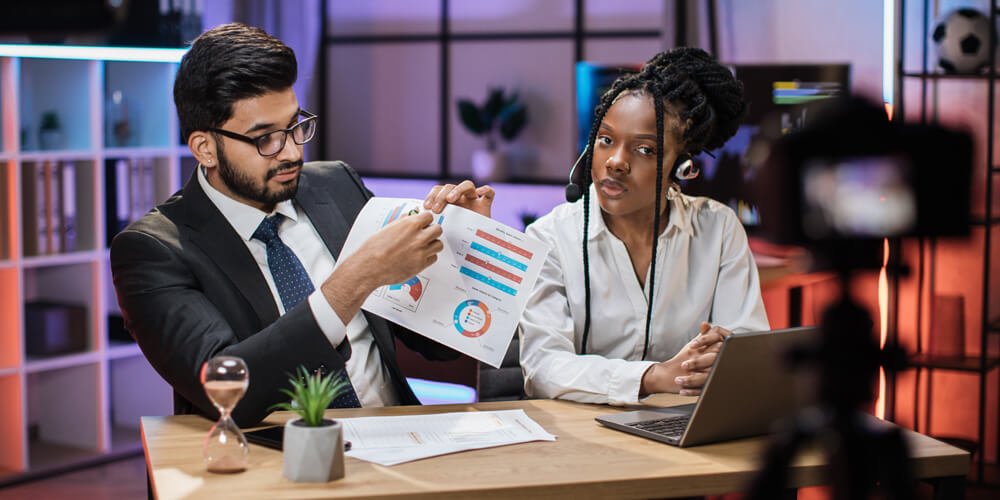

Programming Languages Used in Android Development
The Advantage of Working with Us
Android development supports multiple programming languages, giving developers the flexibility to choose based on their skillset and project requirements.
175K+
project complete
345+
client relations
126K+
customer service
full services

Android App Architecture
Well-structured architecture ensures scalability, testability, and maintainability. The Android Architecture Components introduced by Google have become the de-facto standard for building robust applications.
MVVM Architecture
Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) separates the development of the graphical user interface from the development of the business logic.
Model: Represents the data layer, including data sources and repositories.
View: The UI layer which displays data and sends user actions to ViewModel.
ViewModel: Holds UI-related data and business logic.
Jetpack Components
Android Jetpack is a suite of libraries that helps developers follow best practices and write reliable code.
LiveData: Lifecycle-aware data holder.
Room: SQLite object mapping library.
Data Binding: Binds UI components in layouts to data sources.
Navigation: Simplifies navigation within the app.
WorkManager: Manages background tasks.
An Android app is not just a single program but a combination of various components, each with its own lifecycle and responsibilities.
Components of an Android Application

juliana silva
Our Client
Helped me launch my first app in just a few weeks. Highly recommend!

basic plan
Favorite Price
$250,2
/Month
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit, consect
- adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod
- tempor incididunt ut labore
testimonial
Why Clients Trust Us
Testimonial snippets you can use for showcasing feedback on an Android development course, app, or service.


Professional, responsive, and delivered exactly what I needed. Fantastic experience.

Best Practices for Android Developers
Keep UI responsive using background threads for long operations.
Use modern development libraries and frameworks.
Minimize memory usage and avoid memory leaks.
Apply consistent coding standards and documentation.
Follow Google’s Android design and development guidelines.
Regularly update dependencies and SDKs.
Trends in Android Development
The Android ecosystem continues to evolve rapidly. Developers must stay updated to take advantage of new tools and features.
Emerging Trends
Jetpack Compose for declarative UI development
Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile (KMM) for code sharing
AI and ML integration using ML Kit
Augmented Reality with ARCore
Android on foldables and wearables
frequently asked questions


more information?
APK is the traditional Android app package format.
Kotlin is currently the preferred language due to its concise syntax, safety features, and official support by Google. Java is still widely used and supported, especially for legacy projects.
While high-end specs improve build and emulator performance, Android Studio can run on moderate hardware. A quad-core CPU, 8 GB RAM, and SSD are recommended for a smoother experience.
Yes, you can use other IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA, Visual Studio Code, or command-line tools, but Android Studio offers the most comprehensive features for Android development.
Native apps offer better performance and access to device features. Cross-platform tools like Flutter or React Native can speed up development for both Android and iOS but may have limitations.
blog
Follow best practices such as using encrypted storage, HTTPS, securing APIs, minimizing permissions, and regularly updating your dependencies.


